The Preventive Maintenance Dashboard in Excel
Recommandés
The role of the preventive maintenance manager is crucial to ensure the operational efficiency of the company and to avoid unexpected interruptions. Their mission is complex due to the diversity of their tasks. A key challenge is to implement a preventive maintenance model to minimize downtime. That is why the responsibility of the maintenance manager is even greater, given the varied nature of their job.
The challenge for the maintenance manager: Improve efficiency and reduce unexpected downtimes through preventive maintenance.
Also read:
- Predictive Maintenance Dashboard
- 6 Preventive Maintenance Plan Templates
- Preventive Maintenance Plan in Excel
- Simple Guide for Developing a Preventive Maintenance Plan
- Maintenance Intervention Report Template
- Maintenance Checklist: Definition, Method, Word Example
What is Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance occurs regularly or according to predefined criteria to keep equipment in good working condition. Its primary goal is to reduce the risk of breakdowns in assets, machines, and equipment. It also contributes to broader objectives within the industrial company.
Diverse industries promote the prevalence of preventive maintenance in growing factories and businesses.
IT Preventive Maintenance:
In IT, preventive maintenance covers both software and hardware, as both have a decisive influence on system performance, which in turn affects speed and agility.
For software, there are preventive maintenance programs that scan the system to detect and fix errors and leftover debris from daily use, such as invalid registry entries or missing shortcuts.
Defragmentation is also common—it reorganizes data on the hard drive so that it takes no longer than necessary to read.
For hardware, preventive maintenance usually consists of cleaning the exterior and surroundings to prevent dust and dirt accumulation inside the equipment and its peripherals. Internal cleaning is typically handled by specialized technical staff.
The Role of a Maintenance Manager
The maintenance manager plays a key and cross-functional role within a company. Below is a breakdown of their responsibilities:
Managing and Anticipating the Unexpected
Even with preventive and predictive maintenance, handling unforeseen issues remains a challenge. Responsiveness is always essential.
Maintenance managers must be able to improvise and respond quickly while having tools, materials, and supplies ready to resolve issues swiftly.
Mastering the Maintenance Budget
Another challenge lies in budgeting for the maintenance department, especially managing inventory. It’s crucial to have all necessary spare parts and materials on hand to perform maintenance tasks efficiently without extending scheduled downtimes.
However, overstocking parts can waste capital and resources.
Budgeting must consider all cost types—fixed, variable, direct, or indirect—and aspects like negotiating with suppliers or investing in new tools that add value.
Team Coordination
Organizing maintenance tasks requires leadership and planning skills. The goal is to assign tasks based on each team member’s skill set, preparation, and experience.
As technical profiles vary, collaborative work is vital. The maintenance manager must enable effective communication channels among team members and departments involved in maintenance management.
Effective Time Management
A maintenance manager must juggle:
- Team coordination
- Task assignments
- Meetings with suppliers/distributors
- Answering queries and emails
- Drafting work and maintenance plans
- Responding to unexpected issues
Managing this workload requires fast access to information, documents, diagrams, and photos, which must be easily shareable with the team. Time management is a daily challenge.
Developing a Preventive Maintenance Strategy and Plan
You can develop a preventive maintenance strategy to meet regulatory inspections, carry out recurring tasks, or schedule interventions based on equipment wear and tear.
To develop a preventive maintenance plan:
- Understand the key aspects and necessary tools
- Know the three types of maintenance and their implementation
Summary:
Corrective maintenance solves problems. Preventive maintenance aims to prevent them.
Corrective maintenance occurs after equipment failure. Preventive maintenance uses regular checks to ensure equipment works correctly and detects any issues before failure.
Planning Preventive Maintenance
Before creating a preventive maintenance strategy, understand the proactive approach involving four key action elements:
Inspection, Detection, Correction, Prevention
1. Inspection:
Inspections are vital and serve two main purposes:
- Ensuring safe use of equipment and reducing workplace injuries
- Protecting machines by ensuring they function as intended
2. Detection:
A run-to-failure approach is costly. Preventive maintenance helps detect problems early, making them easier and cheaper to fix.
3. Correction:
Maintenance staff can proactively resolve detected issues before they worsen or cause disruptions.
4. Prevention:
Combining inspection records and notes allows learning from past mistakes and preventing recurring issues.
Preventing asset failure reduces stress and increases team productivity.
When equipment works as expected, the team can focus on proactive (not reactive) tasks.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance helps anticipate failures and avoid unplanned downtimes. Its benefits include:
- Extending equipment lifespan
- Reducing downtime
- Ensuring service quality
- Saving resources
When designing a preventive maintenance plan, it’s essential to consider your specific facilities and equipment.
Relying solely on corrective maintenance can jeopardize operations due to prolonged downtime or compromised quality during emergencies.
Elements of a Preventive Maintenance Dashboard
The maintenance checklist in Excel is a detailed listing of all procedures to be carried out as part of the preventive maintenance plan in the spreadsheet software. Such a list is employed to ensure continuous observation of crucial metrics. The amount of time necessary for repairs, the percentage of scheduled upkeep, and the typical periods between failures are closely tracked.
What Are the Principal Indicators of Maintenance?
There are several potential methods for constructing a preventive maintenance dashboard in Excel. Considered fundamental signals utilized by industry specialists are: the portion of time devoted to planned servicing versus unexpected repairs, a measurement of equipment productivity accounting for quality, performance, and availability, the common time expected to mend repairable parts including fixing, testing and return to regular operation, and the anticipated period between one malfunction and the subsequent during regular function. Compliance with scheduled preventive maintenance tasks completed within a given timeframe is another potential metric.
It is also feasible—as with many things—to access ready-made templates for managing care plans, particularly preventive upkeep. This solution suits many project administrators responsible for scheduling and planning maintenance. The finest choice in this scenario involves using Excel Macros, permitting access to the most appropriate templates. These tools allow automated oversight of all assets, clear records of variables in the plans, and control of servicing for each piece of equipment, among other benefits.
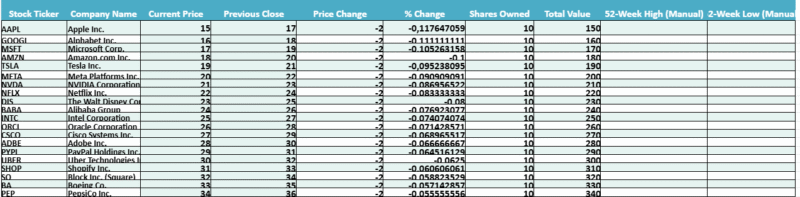
Preventive Maintenance Dashboard
Task List – Preventive Maintenance Dashboard (Example)
Application:
Here is an example with figures to illustrate these preventive maintenance indicators:
Let’s say that in a factory, during a given month, maintenance activities were tracked and measured as follows:
Example: Preventive Maintenance Indicators with Data
Let’s consider a factory scenario where maintenance activities were measured over the course of one month. The key indicators are as follows:
- Total Planned Maintenance Time:
120 hours - Total Unplanned Maintenance Time:
30 hours - Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE):
85%
→ Indicates the equipment was operational for 85% of the month. The remaining 15% represents downtime for maintenance. - Mean Time to Repair (MTTR):
2 hours
→ On average, it takes 2 hours to complete repairs during maintenance activities. - Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF):
200 hours
→ On average, 200 hours pass between two equipment breakdowns during regular operation. - Preventive Maintenance Compliance (PMC):
90%
→ 90% of all scheduled preventive maintenance tasks were completed on time.
These figures provide an overview of preventive maintenance performance in the factory for the month in question. They help measure maintenance effectiveness and identify potential areas for improvement.
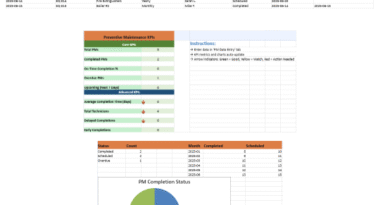
Preventive Maintenance Dashboard – Basic Template
A Preventive Maintenance Dashboard in Excel enables managers to track key indicators that reflect maintenance effectiveness. The dashboard shows current values versus target benchmarks for metrics such as:
- Planned maintenance completion percentage
- Overall equipment uptime
Regular updates using data from maintenance reports allow teams to evaluate work quality and identify issues that need attention.
While the summary provides a concise overview, deeper analysis is essential. Reviewing trends in indicators like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) across multiple periods reveals how the maintenance plan is performing. Comparing current data with past results highlights strengths and areas for improvement. A preventive maintenance checklist supports continuous, proactive efforts aligned with production goals.
Practical Example: Preventive Maintenance Plan for Vacation Rentals
Creating a preventive maintenance plan for vacation rental properties involves a methodical combination of routine inspections and long-term planning. This ensures high guest satisfaction and keeps facilities in optimal condition.
Step 1: Identify Key Areas
Focus on zones requiring regular upkeep:
- Exteriors: roof, paint, garden, lighting
- Interiors: kitchen appliances, bath fixtures, furniture
- Systems: plumbing, HVAC, electrical
Step 2: Create a Task Checklist
Assign specific tasks to each area:
- Roof: inspect and clean gutters (semi-annual)
- HVAC: check and service (annual)
- Garden: landscape upkeep (monthly)
- Safety Devices: test alarms and detectors (monthly)
Use this checklist to:
- Catch issues early
- Prevent costly repairs
- Maintain a repair budget
- Reassess and update annually
Step 3: Scheduling
Assign frequencies (monthly, quarterly, etc.) and use a calendar or task manager to track them. Schedule critical tasks during high-traffic periods.
Step 4: Assign Responsibilities
Allocate tasks to internal staff or external vendors. Ensure each person:
- Understands the task
- Knows the timeline
- Can break down complex duties into actionable steps
Step 5: Monitor and Update
Track progress and maintenance history through:
- A digital dashboard with charts and KPIs
- A spreadsheet with filters and color formatting
- Property management software
Example Maintenance Table
| Location | Task | Frequency | Accountable Party | Last Done | Next Due | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roof | Gutter inspection & cleaning | Semi-annual | Contractor | May 2023 | Nov 2023 | Modernization planned |
| Heating System | Service & check | Annual | In-house team | Sep 2023 | Sep 2024 | Replace filters & control panel |
| Garden | Landscape upkeep | Monthly | Gardener | June 2023 | July 2023 | Attention needed on hedges & lighting |
Tools & Resources
- Project Tools: Trello, Asana, Google Calendar
- Property Management Apps: Maintenance-specific modules for better tracking
Practical Guide: Creating a Preventive Maintenance Dashboard in Excel
To manage maintenance efficiently in Excel:
Step 1: Define Your KPIs
- % of Tasks Completed On Time
- Average Maintenance Cost per Asset
- Equipment Failure Rate
- Average Repair Duration
Step 2: Structure the Dashboard
Organize your Excel file into four key areas:
- Asset Registry – asset name, type, location, purchase date
- Maintenance Schedule – asset, planned date, task, frequency, status
- KPI Tracker – automatic formulas for indicators
- Summary Sheet – overview with trends and overdue items
Step 3: Automate KPI Calculations
Use Excel formulas:
% Tasks Completed:=COUNTIF(StatusRange, "Done") / COUNTA(StatusRange)Avg. Cost per Asset:=SUM(CostRange) / COUNTA(AssetRange)
Helpful functions: SUMIFS, AVERAGEIFS, COUNTIFS
Step 4: Enable Auto-Updates
- Use Excel Tables for dynamic data expansion
- Add VBA Macros for importing data or sending alerts
Step 5: Build a Summary Sheet
- Include bar charts, pie charts, and status dashboards
- Create interactive filters using pivot tables or slicers
Step 6: Best Practices
- Data Validation: Control date, cost, and status entries
- Sheet Protection: Lock formulas and formats to avoid accidental changes
Advanced KPIs to Track
| KPI | Formula | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Reliability Rate | (Uptime Periods / Total Observation Periods) × 100 | How often equipment operates without issues |
| MTBF | Total Operating Time / Number of Failures | Avg. time between equipment failures |
| MTTR | Total Repair Time / Number of Repairs | Avg. time taken to fix equipment |
| Availability Rate | (MTBF / (MTBF + MTTR)) × 100 | % time equipment is available and operational |
Charts and Visual Dashboard
- Line Charts: Visualize MTBF and MTTR trends over time
- Bar Graphs: Track cost per asset or task completion rate
- Pie Charts: Show distribution of task statuses (e.g., planned vs completed)
- Dynamic Dashboard: Combine visuals in a summary sheet for live tracking
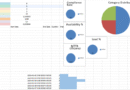
Preventive Maintenance Dashboard in Excel – Example
🔧 Core Purpose
To track, analyze, and visualize maintenance activities through key performance indicators (KPIs), real-time user data, and auto-updated charts — empowering proactive asset management.
🗂️ Included Worksheets
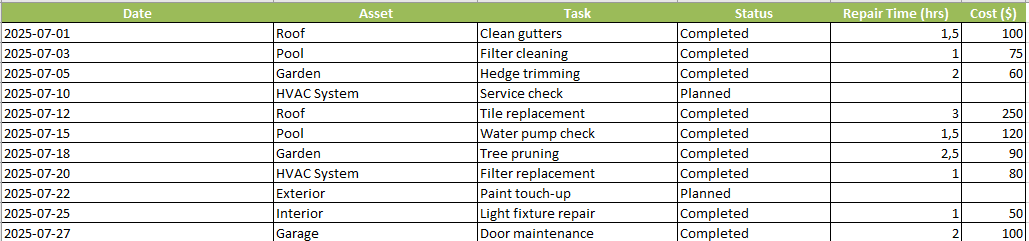
1. User Data Entry
- A structured form for logging maintenance activity
- Fields:
Date,Asset,Task,Status,Repair Time (hrs),Cost ($) - Color-coded header row for ease of use
- Pre-filled with realistic data (e.g., Pool filter cleaning, Roof tile replacement)
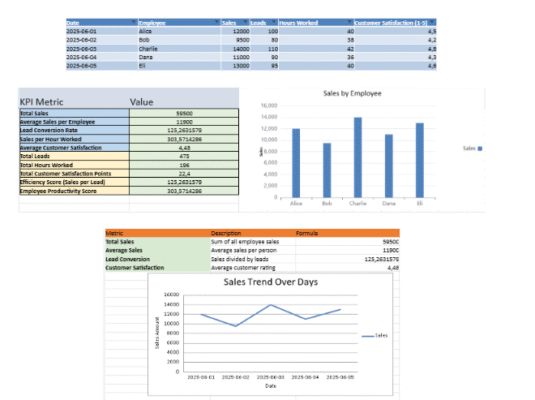
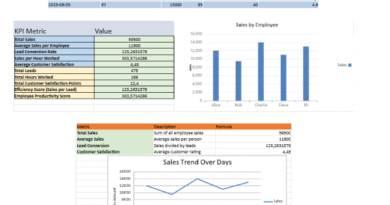
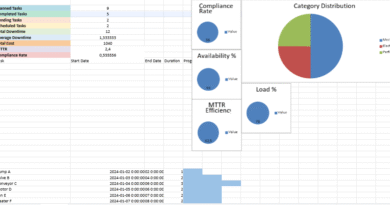
2. KPI Tracking
- Automatically calculated performance indicators, including:
- ✅ % Tasks Completed
- ⏱️ Average Repair Time
- 💰 Average Maintenance Cost
- 🛠️ Total Maintenance Cost
- 📊 Total Completed vs Planned Tasks
- Includes an Alerts Section:
- Flags if average repair time exceeds 2 hours
- Notes if any tasks are still marked “Planned”
3. Maintenance Schedule
- Tracks future and past maintenance by:
Asset,Planned Date,Task Description,Frequency, andStatus
- Supports planning across months or seasons
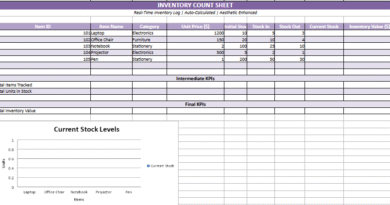
4. Asset Inventory
- Lists physical assets with:
Name,Location,Type, andPurchase Date
- Helps associate maintenance tasks with specific resources
📈 Integrated Charts and Visualizations
✔️ Pie Chart – Task Status Distribution
- Visual breakdown of completed vs planned tasks
- Automatically updates from user entry data
📉 Line Chart – Cost Over Time
- Shows trend of repair costs across maintenance dates
- Highlights spikes in spending for better budgeting
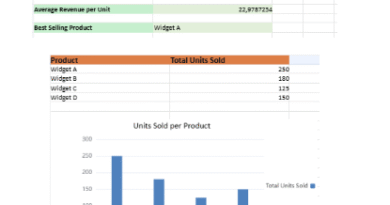
📊 Bar Chart – Task Status Summary
- Compares number of completed vs planned tasks
- Helps evaluate team efficiency and backlog
⚙️ Automation and Calculation Features
- Formulas auto-calculate key KPIs using live data
- Charts update dynamically as data is entered
- Data validation ensures clean entry (e.g., dates, numeric values)
✅ Use Cases
This dashboard is ideal for:
- Vacation property managers
- Maintenance supervisors
- Facility coordinators tracking repair tasks, costs, and equipment health