Preventive Maintenance Checklist Printable : Structure, Value, and Implementation
Recommandés
A preventive maintenance checklist is not just a document—it’s a framework. It ensures that every machine, tool, or safety system is maintained before failure occurs. Unlike corrective maintenance, which reacts to breakdowns, preventive maintenance keeps operations running without interruption.
📋 What Is a Preventive Maintenance Checklist?
This checklist is a structured list of routine tasks that must be completed on a regular basis. Each task relates to a specific machine, area, or safety component.
A typical checklist includes:
- Task description (e.g. inspect belts, test emergency stops)
- Frequency (daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly)
- Status (done or not done)
- Date and responsible technician
- Additional remarks if anomalies are found
Some templates also include checkboxes, automated summaries, and visual indicators to make reporting easier and faster.
🔧 Why Is It Crucial?
Without tracking maintenance tasks, even basic issues can evolve into costly shutdowns. A checklist prevents that by creating a repeatable process.
Key advantages:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Consistency | Tasks are repeated on a fixed schedule |
| 🛑 Risk reduction | Prevents unexpected machine failures |
| 🔍 Traceability | Records who did what, when, and why |
| 📈 Data-driven improvements | Highlights recurring issues or delays |
| 📂 Compliance | Supports internal audits and external inspections |
How to Build a Functional Checklist
Building an effective checklist involves more than listing tasks. It must follow the flow of actual maintenance procedures and be simple enough to use daily.
Start with these steps:
- Identify critical equipment
- Prioritize machinery whose failure would impact operations.
- Define realistic frequencies
- Avoid overload. Match tasks to technical need, not guesswork.
- Break down the task clearly
- “Lubricate bearings” is better than “Do maintenance.”
- Assign responsibility
- Every row should tie to a technician or team.
- Test usability
- A good checklist should be easy to read, quick to fill, and hard to misinterpret.
Optional additions:
- Columns for week/month tracking
- Conditional formatting (e.g. red if “No”, green if “Yes”)
- Digital signature or QR code for secure validation
Monthly Reporting With a Checklist
A checklist becomes a powerful source of insight when paired with a monthly summary. Maintenance teams can extract:
- Total tasks scheduled vs. completed
- Top 5 most delayed actions
- Common remarks across equipment types
- Status of preventive vs. corrective actions
Modern templates can automate this in Excel with formulas, dropdowns, and status visuals—giving real-time visibility to supervisors and safety officers.
Download a Ready-Made Template
To save time, you can start with a fully formatted Excel template including:
- ✔️ 22 pre-filled maintenance tasks
- 📆 Weekly and monthly tracking
- 🎨 Colored headers and visual status indicators
- 📈 Monthly summary sheet, ready to print or share
📥
The value of a preventive maintenance checklist lies in its discipline and simplicity. When used correctly, it removes uncertainty, reduces breakdowns, and supports a culture of operational reliability. It’s not paperwork—it’s prevention made visible.
🔧 Master Preventive Maintenance Checklist & Monthly Tracking Template
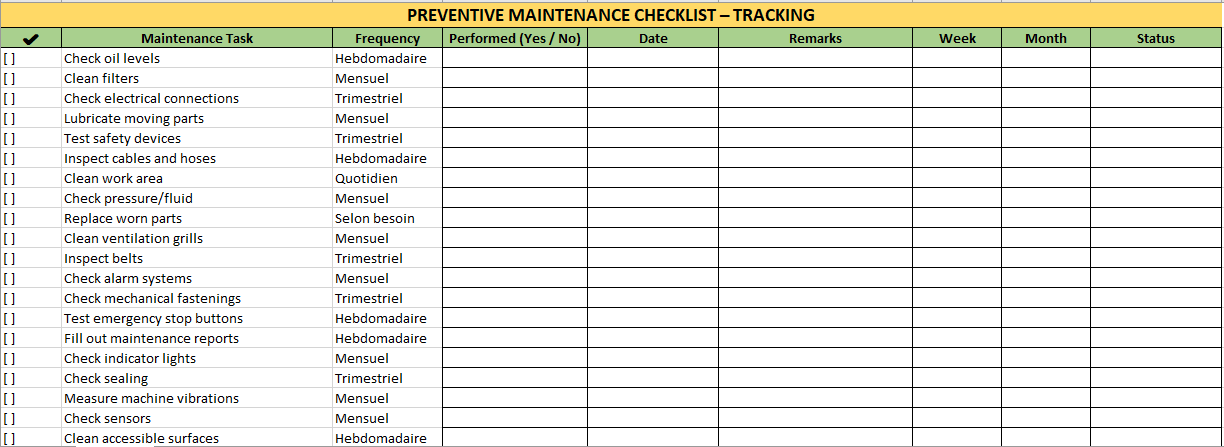
The Excel sheet created — titled “Preventive Maintenance Checklist – Tracking” — is a ready-to-use, structured tool designed for real-world maintenance environments. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its contents and layout:
🧾 Sheet 1: Checklist
Structure:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ✔ | Simulated checkbox for easy ticking |
| Maintenance Task | Clearly defined task (e.g. “Check oil levels”, “Clean filters”) |
| Frequency | Indicates how often the task should be performed (e.g. Weekly, Monthly) |
| Performed (Yes / No) | Technician marks if the task was completed |
| Date | Date of execution or inspection |
| Remarks | Notes on any issues, delays, or observations |
| Week | Number of the week or range (e.g. W27) |
| Month | Month of execution (e.g. July) |
| Status | Visual feedback (color-coded: ✅ green for “Yes”, ❌ red for “No”) |
Visual Features:
- 🔶 Color-coded title bar (“PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE CHECKLIST – TRACKING”)
- ✅ Conditional formatting turns the “Performed” column:
- Green when marked “Yes”
- Red when marked “No”
- 📥 Simulated checkboxes in column A for manual ticking (can be used digitally or printed)
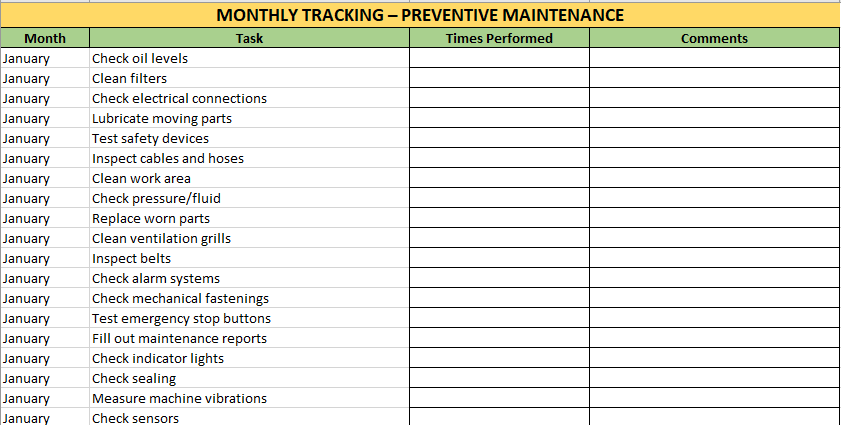
📄 Sheet 2: Monthly Summary
Structure:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Month | Lists months (January to June) |
| Task | Corresponds to tasks listed in the checklist |
| Times Performed | Cell to enter how many times the task was completed in the month |
| Comments | Space to add context, irregularities, or explanations |
📊 Visual Features:
- 🔷 Colored header: “MONTHLY TRACKING – PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE”
- Columns are spaced and formatted for printing or digital entry
✅ Purpose and Use Cases:
- 🏭 Industrial machinery upkeep
- 🧰 Equipment room inspections
- 🧪 Lab equipment preventive checks
- 🛠 Facilities management routines
📦 File Specs:
- Format:
.xlsx(fully editable) - Sheets: 2
Checklist(interactive tracking)Monthly Summary(reporting dashboard)
- Designed for use with Excel 2016+, LibreOffice, or Google Sheets
Preventive Maintenance Approach: A Structured, Proactive Strategy
A preventive maintenance (PM) approach is built on one core idea:
👉 Don’t wait for equipment to fail—act before it does.
This approach blends planning, routine action, and tracking, creating a loop of reliability that protects productivity, reduces downtime, and extends asset lifespan.
1. Objective-Based Planning
Before launching a PM plan, define what you aim to prevent or improve:
- Reduce unexpected machine failures
- Avoid costly emergency repairs
- Improve equipment availability
- Stay compliant with safety standards
These goals shape the scope of your checklist and frequencies.
2. 🧩 Equipment Risk Prioritization
Not all machines require the same attention. The PM approach starts with criticality analysis:
| Priority Level | Examples | Action |
|---|---|---|
| High | HVAC, electrical panels, pumps | Weekly or monthly checks |
| Medium | Lighting, sensors, belts | Monthly or quarterly checks |
| Low | Cabinets, display screens | Visual check as needed |
This ensures resources are spent where they matter most.
3. 🛠️ Standardized Task Definition
Each PM task must be:
- Specific: “Lubricate belt” instead of “Maintenance”
- Measurable: Include frequency, expected state
- Repeatable: Executable by any trained technician
- Documentable: Result logged clearly
Standardization ensures consistency even across shifts or teams.
4. 📅 Scheduled Execution
Set up a routine cycle with:
- Weekly/monthly checklists based on task criticality
- ⏱ Time slots for execution integrated into shift planning
- 👷 Assigned responsibilities for each technician or role
Automated checklists (e.g. in Excel or CMMS) make this easier to track and update.
5. 🧾 Traceability and Reporting
Every completed action should leave a trail:
- ✔️ Checkboxes for done/undone tasks
- 🖊️ Technician initials or digital signature
- 📆 Timestamp
- 📋 Comment section for observations or anomalies
This data feeds into a monthly report that highlights:
- Completion rates
- Missed tasks
- Recurring issues
- Equipment flagged for repair or replacement
6. 🔄 Feedback and Adjustment Loop
Preventive maintenance is dynamic:
- Modify checklists if equipment is upgraded or removed
- Adjust frequencies based on actual wear trends
- Use feedback from technicians to refine task clarity
PM isn’t a static checklist—it’s an evolving system that learns over time.
Mindset: From Task to Culture
A successful PM approach is not just technical—it’s cultural.
- Operators should feel responsible for early detection.
- Managers should support routine over reaction.
- The checklist should feel like a tool, not a chore.
Here’s a clear breakdown of what to check in preventive maintenance, organized by category and based on best practices in industrial, commercial, and technical environments:
🧰 1. Mechanical Components
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Bearings | Lubrication, wear, noise |
| Belts and Chains | Tension, alignment, cracks, fraying |
| Gears and Couplings | Backlash, lubrication, alignment |
| Moving Parts (shafts, joints) | Smooth motion, unusual vibration |
| Fasteners and Mounts | Looseness, corrosion, missing parts |
⚡ 2. Electrical Components
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Power Cables | Insulation integrity, wear, tension |
| Plugs and Sockets | Secure fit, damage, overheating |
| Circuit Breakers / Fuses | Operation test, condition, tripping |
| Sensors and Switches | Response, accuracy, proper mounting |
| Control Panels | Cleanliness, indicator lights, overheating |
🔩 3. Hydraulic / Pneumatic Systems
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Hoses and Fittings | Leaks, cracks, pressure loss |
| Reservoir Levels | Oil, coolant, or hydraulic fluid levels |
| Filters | Clogging, pressure drop |
| Actuators and Cylinders | Speed, alignment, response time |
| Pressure Gauges / Valves | Calibration, leaks, blockage |
🌬️ 4. Air Handling / Ventilation
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Air Filters | Clogging, replacement date |
| Ducts and Vents | Blockages, mold, dust buildup |
| Fans and Blowers | Noise, imbalance, airflow |
| Temperature/Humidity Sensors | Accuracy, calibration |
🔥 5. Safety Systems
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Emergency Stop Buttons | Activation, location visibility |
| Alarms and Buzzers | Sound level, responsiveness |
| Fire Extinguishers | Pressure gauge, seals, accessibility |
| Safety Guards / Covers | Proper installation, no damage |
| PPE Stations / Labels | Legibility, expiration, completeness |
💻 6. Digital & Control Systems
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| PLC / HMI Panels | Display clarity, functionality |
| Software Versions | Update status, backup availability |
| Data Logging Systems | Correct logging, timestamp errors |
| Communication Interfaces | Cables, connectors, signal integrity |
🧹 7. General Condition & Cleanliness
| Item to Check | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Equipment Cleanliness | Dust, oil, residue buildup |
| Floor / Area Cleanliness | No slips, debris, oil spills |
| Lighting | Intensity, flickering, accessibility |
| Warning Signs / Markings | Clear visibility, non-worn labels |
✅ Frequency Tips:
| Frequency | Typical Tasks |
|---|---|
| Daily | Clean workspace, check emergency stops, inspect visually |
| Weekly | Lube moving parts, test alarms, inspect belts |
| Monthly | Clean filters, check gauges, electrical spot check |
| Quarterly | Full inspection, update backups, check calibration |
| Annually | Deep maintenance, refurbishments, professional audits |